The world of real estate investing often seems like a straightforward path to wealth, but the reality is far more nuanced. According to the National Association of Realtors, the median home price in the United States has increased by over 100% in the past 20 years, highlighting the potential for substantial returns. However, a staggering 60% of investors fail to achieve their financial goals due to poor investment decisions. This is where real estate investment property analysis comes into play, providing a systematic framework to evaluate opportunities and mitigate risk.
While real estate investing offers the potential for significant returns, it’s crucial to understand that success is not guaranteed. Market fluctuations, economic downturns, and unforeseen events can all impact investment outcomes. Therefore, a thorough analysis is essential to mitigate risks and make informed decisions. Navigating the complexities of real estate investing requires a clear understanding of market dynamics, property attributes, and financial implications. Just as a sailor needs a compass and a map to navigate the open sea, investors need a systematic framework to guide their investment decisions.
This guide will empower you to confidently navigate the often turbulent waters of real estate investing, helping you unlock profitable opportunities and achieve your financial goals.
Understanding the Basics of Real Estate Investment Property Analysis
Real estate investment property analysis is the systematic evaluation of a property’s financial viability as an investment. This process considers various factors, including potential income generation, appreciation, and overall profitability. A thorough analysis is vital for identifying promising opportunities, avoiding costly mistakes, and making informed decisions about capital allocation.
What is Real Estate Investment Property Analysis?
This analysis is not just about crunching numbers; it’s about understanding the market dynamics and the specific attributes of the property. Investors who grasp the fundamentals of this analysis can make strategic choices that align with their financial goals. Essentially, it serves as a roadmap for success, guiding you through the often turbulent waters of real estate investment.
Why is Property Analysis Essential?
- Identifying Opportunities: A well-conducted analysis can reveal undervalued properties with high potential for appreciation and income generation.
- Avoiding Mistakes: Understanding the financial implications helps prevent poor investment choices that could lead to significant losses.
- Informed Decision-Making: With accurate data, investors can allocate capital more effectively, ensuring their investments align with their financial objectives.
Key Metrics Covered
- Cash Flow: The net amount of cash generated from rental income after deducting expenses. Positive cash flow indicates a profitable investment.
- Capitalization Rate (Cap Rate): A measure of a property’s profitability based on its net operating income (NOI) relative to its market value. It helps investors compare the profitability of different properties.
- Return on Investment (ROI): A comprehensive metric that evaluates the overall profitability of an investment, considering both cash flow and property appreciation.
Essential Steps for Analyzing an Investment Property
Now, let’s break down the key steps involved in a comprehensive investment property analysis. Each step is crucial for ensuring you make a sound investment decision.
Step 1: Determine Market Value
Understanding the true worth of a property is foundational to your analysis. An accurate market valuation informs whether the asking price is justified and sets the stage for evaluating potential returns.
Methods for Assessing Market Value
-
Comparative Market Analysis (CMA): This method involves evaluating the sale prices of similar properties in the area. By analyzing recent sales, you can gauge what buyers are willing to pay. It’s essential to focus on properties that are similar in size, condition, and location to ensure a fair comparison.
-
Financial Metrics: Utilize metrics like the capitalization rate (cap rate) and gross rent multiplier (GRM) to assess property value. These figures help you understand how well a property can generate income relative to its price. For instance, if a property has a cap rate of 10% and a market value of $200,000, its net operating income (NOI) would be $20,000.
-
The 1% Rule: This rule suggests that a property’s monthly rent should ideally be at least 1% of its purchase price. For example, if a property is listed for $200,000, it should generate around $2,000 in monthly rent. While this can serve as a useful starting point, it’s crucial to remember that the 1% rule is a general guideline and may not be applicable in all situations.
Conducting Market Research
-
Online Resources: Websites like Zillow, Realtor.com, and Redfin can provide valuable data on property values and market trends. These platforms often include historical data, neighborhood statistics, and other relevant information that can aid your analysis.
-
Local Real Estate Professionals: Consult with agents and brokers who have experience in the local market. Their insights can provide a deeper understanding of market dynamics and help you make more informed decisions.
-
Comparable Properties: Analyze similar properties to understand pricing trends and demand. This can provide context for your valuation and help identify whether a property is overpriced or a bargain.

Step 2: Calculate the Cost of Owning the Property
Owning a property entails costs that extend beyond the purchase price. Understanding these expenses is crucial for accurately projecting profitability.
Common Ownership Expenses
-
Property Taxes: Annual taxes imposed by local governments can vary significantly based on location and property type. For example, property taxes in a specific area might range from 1% to 2% of the property’s assessed value.
-
Insurance Costs: Coverage for property damage and liability is essential for protecting your investment. Different types of insurance may be required, including landlord insurance, which covers specific risks associated with rental properties. Insurance costs can vary based on the property’s size, location, and coverage options.
-
Maintenance Expenses: Regular upkeep and unexpected repairs can add up quickly. It’s wise to budget for routine maintenance as well as potential emergencies, such as plumbing issues or roof replacements.
-
Management Fees: If you hire a property management company, their fees will impact your cash flow. These fees can vary widely, so it’s important to understand what services are included and how they may affect your overall profitability.
The 50% Rule
A common guideline, the 50% Rule posits that operating expenses (excluding the mortgage) will typically amount to about 50% of gross rental income. For instance, if a property generates $30,000 annually, you might estimate $15,000 in expenses. While this can serve as a useful starting point, conducting detailed research and consulting historical data is essential for accuracy.
Step 3: Research Market Rents
Understanding potential rental income is vital for projecting cash flow and assessing the property’s viability as an investment.
Methods for Researching Market Rents
-
Online Resources: Platforms like Rentometer, Zumper, Apartments.com, and Rent.com can help you gauge market rents. These resources often provide insights into average rental prices in specific neighborhoods, making it easier to set competitive rates.
-
“Secret Shopping”: Visiting similar rental properties in the area can provide firsthand information about rental rates, amenities, and tenant demographics. This can help you understand what tenants are willing to pay and how to position your property competitively.

Factors to Consider
-
Local Demand: Are there more tenants than available properties? High demand can justify higher rents. Conversely, if supply exceeds demand, you may need to adjust your expectations.
-
Rental Trends: Investigate whether rental prices are on the rise or decline in your target area. This can affect your future income potential and help you make informed decisions about pricing your property.
Step 4: Estimate Rehab and Updating Costs
Potential renovation needs can significantly influence a property’s profitability. Accurately estimating these costs is crucial for budgeting.
Methods for Estimating Renovation Costs
-
Obtain Quotes: Get estimates from contractors for necessary repairs and updates. This can give you a clearer picture of the financial commitment required to bring the property up to market standards.
-
Research Average Costs: Investigate the typical costs for similar renovations in your area. For instance, replacing a roof might cost between $5,000 and $15,000, depending on the size of the property and the type of roofing material. Understanding local pricing can help you avoid overestimating or underestimating your budget.
-
Consult Property Managers: They can provide insights on common issues and their associated costs. Property managers often have experience with various properties and can offer valuable advice on potential renovations.

Factors to Consider
-
Scope of Work: Identify what repairs or updates are essential. A thorough inspection, potentially with the help of a professional inspector, can uncover hidden issues that may require immediate attention and significantly impact renovation costs.
-
Local Labor Costs: These can vary widely based on location, making it important to understand local rates. Knowing the going rates for labor can help you budget more accurately and avoid surprises.
Key Financial Metrics for Evaluating Investment Properties
Now that we’ve covered the essential steps, let’s delve into the key financial metrics that will help you quantify the profitability of your potential investment.
Cash Flow
Cash flow is the lifeblood of your real estate investment. It’s the difference between your rental income and expenses, representing the amount of money you will receive regularly. It’s a primary indicator of profitability and helps you understand how much money you can expect to generate from the investment.
Calculating Cash Flow
To accurately calculate cash flow, consider the following components:
-
Gross Rental Income: The total amount collected from tenants before any expenses are deducted. This figure represents your potential income and should be projected based on current market rents.
-
Vacancy and Credit Loss: Account for periods when the property may be vacant or tenants may not pay rent. It’s advisable to estimate this conservatively, perhaps by assuming a vacancy rate of 5-10%.
-
Property Management Fees: If you hire a property management company, include their fees in your calculations. These fees can range from 5% to 10% of gross rental income.
-
Maintenance Expenses: Regular upkeep and unexpected repairs should be factored into your cash flow. Consider setting aside a percentage of your income for these costs.
-
Utilities and HOA Fees: These can represent significant costs, especially in multi-family properties. Ensure you know which utilities are covered by the tenant and which are your responsibility.
-
Mortgage Payments: Include principal, interest, property taxes, and insurance in your calculations. Understanding your total mortgage obligation is crucial for accurately forecasting cash flow.
Accurately Forecasting Cash Flow
To forecast cash flow effectively, research historical data, local market trends, and consult with property managers. Using a cash flow analysis spreadsheet can simplify this process and help you visualize your income and expenses.
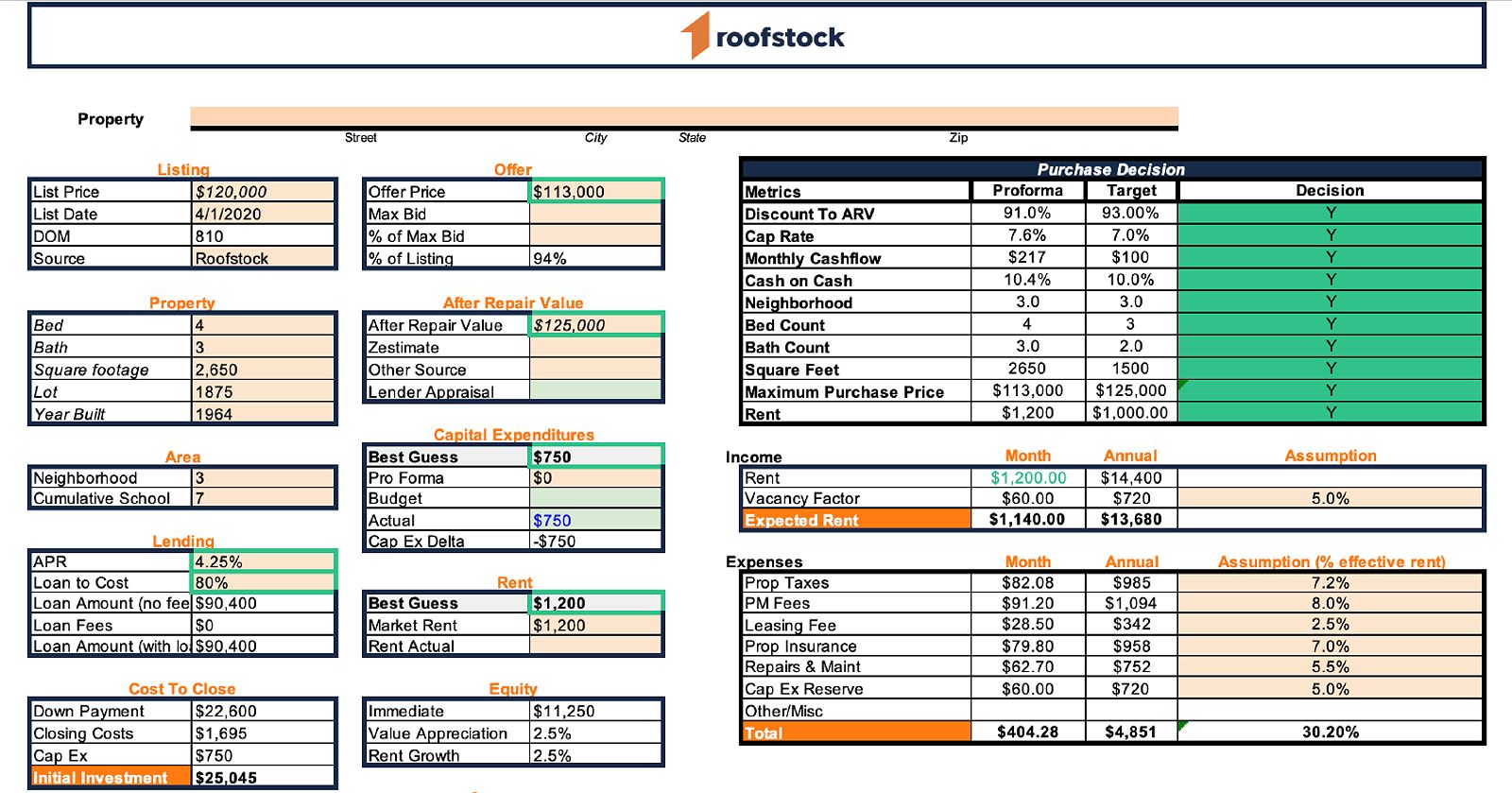
Capitalization Rate (Cap Rate)
The capitalization rate, or cap rate, is a crucial measure of a property’s profitability based on its net operating income (NOI) relative to its market value.
Calculating Cap Rate
To calculate the cap rate, use the formula: Cap Rate = NOI / Market Value. The net operating income is calculated by subtracting operating expenses from gross rental income.
Significance of Cap Rate
Cap rates help you compare the profitability of different properties. Generally, higher cap rates indicate more attractive returns. A typical cap rate range is between 8% and 12%, but this can vary depending on market conditions and property type. It’s crucial to compare cap rates of similar properties in the same area to gain meaningful insights.
Return on Investment (ROI)
Return on investment (ROI) is a measure of the overall profitability of your investment, considering both cash flow and property appreciation.
Calculating ROI
To calculate ROI, use the formula: ROI = (Net Profit / Total Investment) x 100. This metric provides a percentage that represents your investment’s efficiency.
Importance of ROI
Evaluating ROI provides insights into the long-term performance of your investment property. For example, if you invested $100,000 and generated a net profit of $10,000 in a year, your ROI would be 10%. This metric allows you to gauge the effectiveness of your investment strategy and compare it with other potential investments.
Making Informed Investment Decisions
Now that you have a solid understanding of the key metrics and steps involved in analyzing investment properties, let’s discuss how to use this information to make informed decisions.
Set Clear Investment Goals
Having clear investment goals is crucial for identifying properties that align with your financial objectives and risk tolerance.
Common Investment Goals
- Passive Income: Generate regular rental income that provides financial stability.
- Capital Appreciation: Increase the value of the property over time, allowing for profitable resale.
- Tax Benefits: Utilize tax deductions and depreciation benefits to enhance your overall returns.
- Diversification: Spread investments across different asset classes to minimize risk and enhance portfolio stability.
Consider Market Trends and Conditions
Understanding market trends and economic conditions is vital for identifying areas with strong rental demand and potential appreciation.
Factors to Consider
-
Population Growth: Areas with growing populations often see higher demand for rental properties. This trend can lead to increased rental rates and property values.
-
Employment Rates: Strong job markets can support higher rental rates. Higher employment levels generally correlate with increased demand for rental properties.
-
Local Regulations: Be aware of zoning laws and rental restrictions that could impact your investment strategy. Understanding local regulations is crucial for navigating potential challenges.
-
Economic Indicators: Monitor factors like GDP growth, inflation rates, and interest rates. These indicators can provide insights into the overall health of the real estate market and help you make informed decisions.
Seek Professional Advice
Working with real estate professionals can provide invaluable insights, market analysis, and guidance on navigating the investment process.
Real Estate Professionals to Consider
-
Real Estate Agents: They can help you find properties, negotiate purchase prices, and understand local market conditions. A knowledgeable agent can be an invaluable asset in your investment journey.
-
Brokers: Offer expertise in financing options, property management, and legal matters. They can help you navigate complex transactions and ensure that your interests are protected.
-
Property Managers: Handle the daily operations of rental properties, including tenant screening, rent collection, and maintenance. A good property manager can alleviate much of the stress associated with property ownership.
-
Financial Advisors: Guide you on investment strategies, risk management, and financial planning. They can help you develop a comprehensive investment strategy that aligns with your long-term goals.
Manage Risk and Protect Your Investment
Investing in real estate involves various risks, including vacancy, tenant issues, and market fluctuations.
Mitigating Risks
-
Thorough Due Diligence: Conduct comprehensive research and inspections before purchasing. This includes reviewing property documents, understanding the local market, and assessing potential risks.
-
Effective Tenant Screening: Implement rigorous processes to minimize the risk of bad tenants. This includes checking credit history, rental history, and conducting background checks.
-
Property Maintenance: Regular upkeep prevents costly repairs and ensures tenant satisfaction. A well-maintained property is more likely to attract and retain quality tenants.
-
Adequate Insurance Coverage: Protect yourself from financial losses due to unforeseen events. Ensure you have the right insurance policies in place to cover various risks associated with property ownership.
FAQ
Q: What are some good resources for learning more about real estate investment property analysis?
A: Numerous resources are available to enhance your real estate investing knowledge, including online courses, books, podcasts, and industry events. Joining real estate investment clubs or networking with experienced investors can also be beneficial.
Q: How can I find a reliable property manager?
A: Seek property managers with a proven track record, positive reviews, and experience managing similar properties. Request references and inquire about their fees and services to ensure they meet your needs.
Q: What are some common mistakes that new investors make?
A: Common mistakes include failing to conduct thorough research, underestimating expenses, not having a clear investment plan, and not seeking professional advice.
Q: How can I get started with real estate investing?
A: You can start with a small investment or consider partnering with an experienced investor. The key is to begin the journey and continue learning and adapting as you gain more experience.
Conclusion
By grasping the fundamentals of real estate investment property analysis, you can make informed decisions, maximize your returns, and achieve your investment goals. As Warren Buffett once said, “The best investment you can make is in yourself.” Start your journey to real estate investment success by applying the steps and metrics discussed in this guide. Don’t hesitate to seek professional advice and explore additional resources to further enhance your knowledge and skills. Taking the time to conduct thorough analysis and research will ultimately lead to more successful investments and a stronger portfolio.
